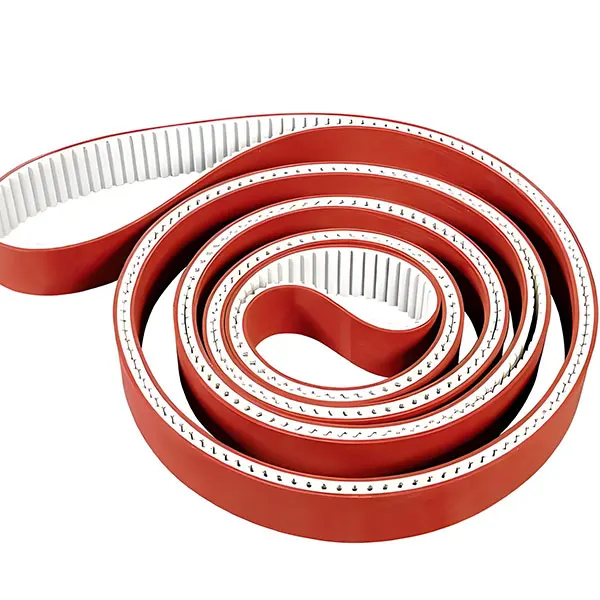
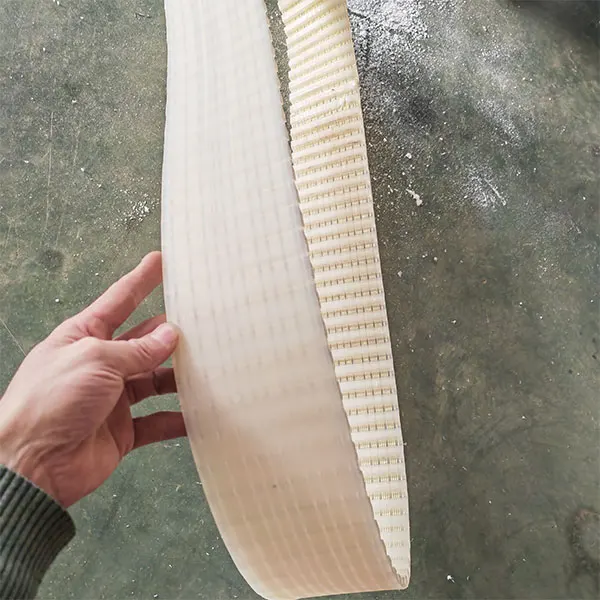
Timing Belt Process Working Machines
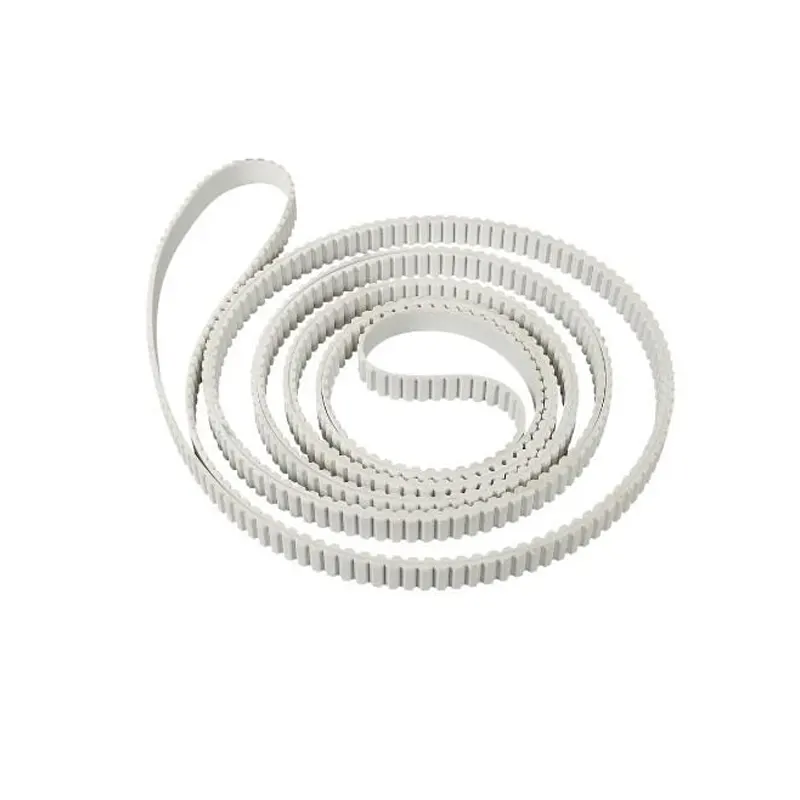
The processing of timing belts is a precision manufacturing process that involves material selection, forming, tooth profile processing, reinforcement layer treatment, and subsequent processes such as edge grinding and surface grinding.
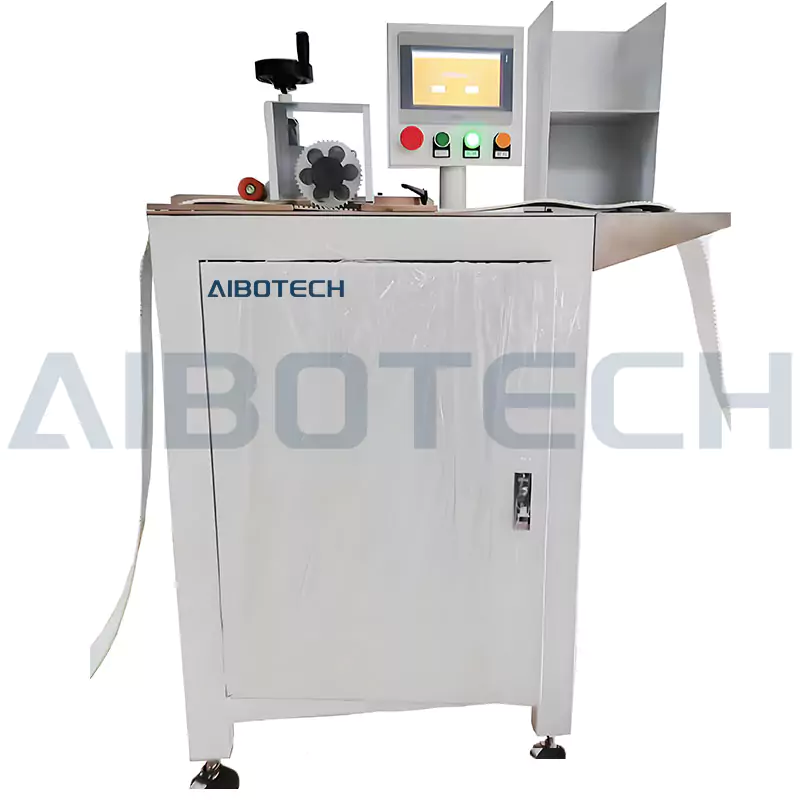
Length Counting (Match Teeth)
The main purpose of tooth counting is to ensure the accuracy of the total number of teeth on the timing belt, in order to meet the design requirements of the transmission system (such as speed ratio, center distance, etc.), while the tooth profile depends more on the machining accuracy of the timing belt (such as molding or cutting process).
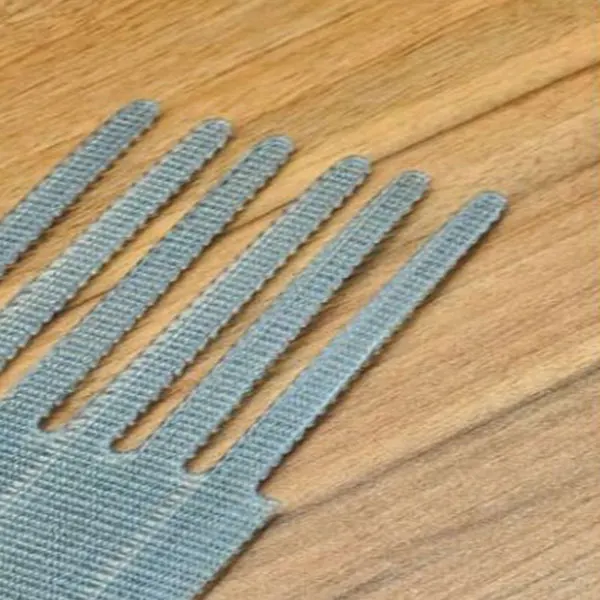
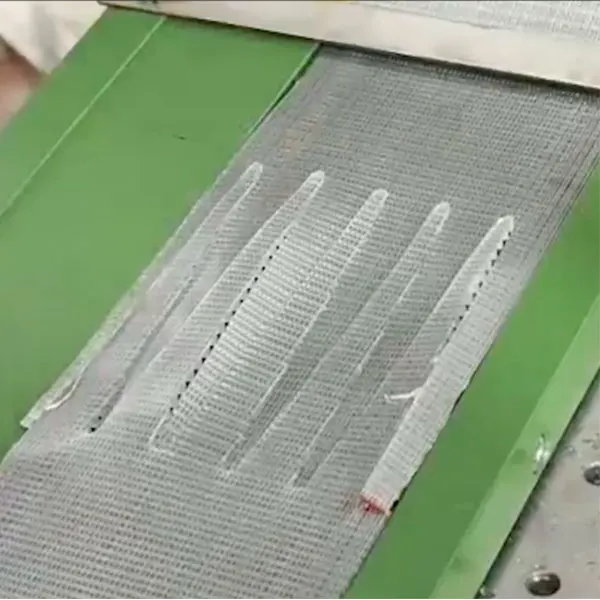
Treatment of Joints (Finger Punching)
The timing belt to be jointed is cut into finger shapes at both ends before splicing is primarily done to enhance splice strength, improve bonding effectiveness, and ensure flexibility and durability at the joint.
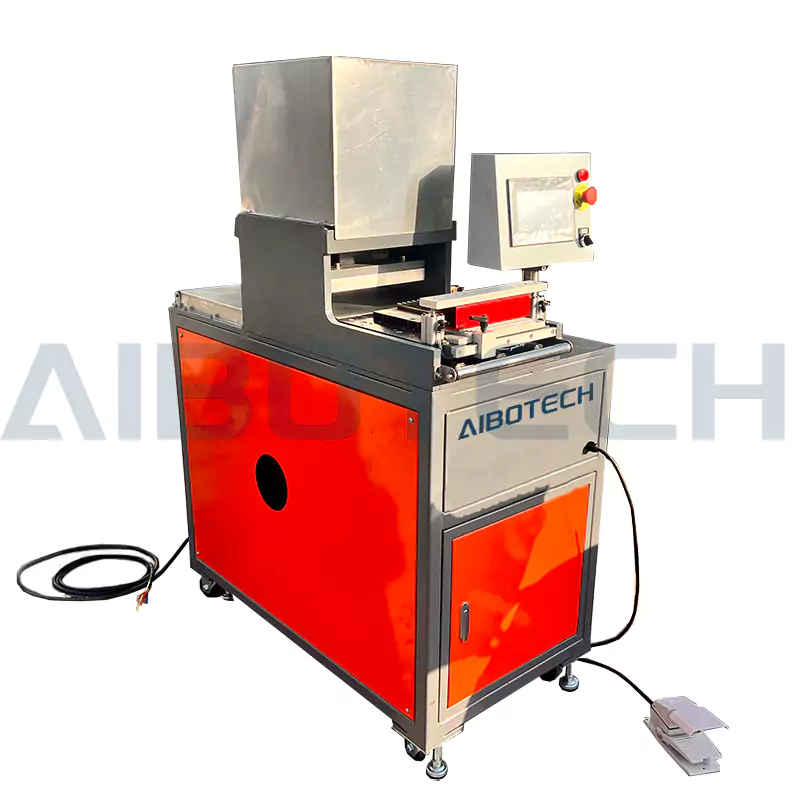
Belt Joint
The hot press joint of a timing belt is a process of joining the two ends of the timing belt into a circular belt through heating and pressure.This joint method can ensure high strength and durability, and is suitable for transmission scenarios that require heavy loads, high speeds, or long lifespans.
Belt Slitting
The slitting of a timing belt is the process of cutting a wide timing belt base (such as a coil or a wide belt blank) into multiple narrow timing belts according to the required size. This process is widely used in the production of multi ribbed belts (multi groove belts) and narrow timing belts (such as 3M, 5M, 8M, etc.), ensuring the width accuracy and edge quality of each timing belt.
Profile Welding Work
Installing the blocks (also known as baffles, guide blocks, or positioning blocks) on the surface of timing belts is mainly to achieve special functional requirements or adapt to specific working conditions. Its core functions include positioning, anti deviation, material conveying, and safety protection.
Timing belt coating work
Applying self-adhesive or pressure-sensitive adhesive on the back of the timing belt is mainly to achieve quick installation, secure additional components, or adapt to special application scenarios.
Milling Teeth Work
The main purpose of double-sided milling of timing belt teeth is to improve transmission accuracy, extend service life, and adapt to special working conditions, improve transmission stability and accuracy. Some equipment (such as automated production lines and reciprocating mechanisms) require the belt to rotate in both directions, and double-sided teeth can ensure the reliability of bidirectional transmission.
Surface and Edge Grinding Machine
Timing belts surface and belt edge grinding is a important work inside the timing belt process work, with the main purpose of optimizing transmission performance, extending service life, and adapting to specific working conditions.
Belt perforating work
Punching (perforation or opening) timing belts is mainly to meet specific functional requirements or adapt to special working conditions, install accessories or fixing requirements, reduce weight and inertia, vacuum adsorption, breathable drainage, heat dissipation and noise reduction, etc